Previtamin Zero
It is the multivitamin supplement with zinc specific for the needs of preterm or low birth weight infants.
Previtamin Zero is the only multivitamin with zinc that, in an importance clinical study pubblished on Amercian Journal of Clinical Nutrition, demonstrates the reducing mortality and morbidity in preterm infants.
The production process of Previtamin Zero takes place in a protective atmosphere and exploits the filling in a nitrogen flow thus ensuring the quality of the product and protecting vitamins from degradation by air.
The particular packaging in glass vial provided with a dropper burnished gravimetric prevents tampering of the product upon exposure to light and reduces contamination.
The new formulation of Previtamin Zero provides the correct supplementation of all the vitamins and zinc, necessary for the growth of preterm or low birth weight infants, in line with the requirements recommended dall’ESPGHAN.
Clinical trials show that zinc is essential for the metabolism of organic, for cell growth and to the immunological defense, and its deficiency has been associated both with an increased risk of respiratory tract infections and intestinal alterations of cognitive development of infants low birth weight for gestational age.
Previtamin Zero contains:
Zinc to help:
- to normal cognitive function and immunity
- the normal DNA synthesis
- the protection of cells from oxidative stress
Vitamin A to help:
- the maintenance of visual acuity
- the normal function of the immune system
Vitamin B1 to help:
- the normal functioning of the nervous systems
Vitamin B2 to help:
- the normal functioning of the nervous systems
- the protection of cells from oxidative stress
- the maintenance of normal visual acuity
Vitamin B3 to help:
- the normal functioning of the nervous systems
Vitamin B6 to help:
- the normal synthesis of cysteine and metabolism of omociytein
- the normal functioning of the nervous system and the immune system
Vitamin B9 (folic acid) to help:
- the normal hematopoiesis
- the normal function of the immune system
Vitamin B12 to help:
- the normal functioning of the nervous system and the immune system
- the processes of formation of red blood cells
Vitamin C to help:
- the normal functioning of the nervous and immune systems
- absorption of iron
- the protection of cells from oxidative stress
Vitamin D3 to help:
- the normal absorption/utilization of calcium and phosphorus
- the maintenance of normal bones and teeth
Vitamin E to protect cells from oxidative stress
Dietary supplements are not intended as a substitute for a varied diet, balanced and healthy lifestyle.
Previtamin Zero has a neutral taste that facilitates the intake by children and does not alter the taste of the milk.
Previtamin Zero does not contain gluten or dyes.
Dosage: 10 drops a day
How to use: Take pure or diluted in water or milk. Shake well before use.
Packaging: Glass bottle burnished 10 ml
Storage: Store at room temperature in a cool, dry place. Avoid exposure to sources of localized heat , direct sunlight and contact with water. The expiration date refers to the product properly stored. Any slight variation in color is not an indication of quality deterioration of the product. Do not throw out in the environment after use.
Warnings: Do not exceed the recommended daily dose . Keep out of the reach of children under 3 years old. Dietary supplements are not intended as a substitute for diet, therefore it is recommended to follow a varied and balanced diet and a healthy lifestyle.
Ingredients: Purified water; zinc sulfate; potassium phosphate dibasic; vitamin C; emulsifier: E433; vitamin E; vitamin A; Vitamin B3; preservative: E202; vitamin B2; vitamin B1; vitamin B6; sucralose; folic acid; vitamin D3; vitamin B12; stabilizer: xanthan gum. Previtamin Zero does not contain gluten or added coloring.
NUTRITION FACTS
| INGREDIENTS | For 100 ml | For 10 drops | % RDA 10 drops |
| Vitamin C | 2 g | 10 mg | 12,5 |
| Zinc | 1,8 g | 9 mg | 90 |
| Vitamin E | 400 mg | 2 mg | 17 |
| Vitamin B3 | 200 mg | 1 mg | 6 |
| Vitamin A | 120 mg | 600 µg | 75 |
| Vitamin B1 | 20 mg | 0,10 µg | 9 |
| Vitamin B2 | 20 mg | 0,10 µg | 7 |
| Vitamin B6 | 10 mg | 0,05 mg | 4 |
| Folic acid | 10 mg | 50 µg | 25 |
| Vitamin D3 | 4 mg | 20 µg | 400 |
| Vitamin B12 | 60 µg | 0,3 µg | 12 |
The role of zinc in the growth and development of children
Zinc is a metal of great nutritional importance and is particularly necessary in cell replication and in the development of the immune response. It is essential for right fetal growth and development and for the production of milk during lactation, it is extremely necessary during the first year of life when the body is in rapid growth phase. Among the factors deficiency in preterm infants will also include the excessive defecation and poor zinc reserves at birth.
Zinc and growth: the zinc plays an important role in the growth and its action was demonstrated on more than 300 enzymes. Zinc is a component of their structure and participates in their catalytic and regulatory functions. Zinc also interacts with important hormones involved in bone growth such as somatomedin-C, osteocalcin, testosterone, thyroid hormones and insulin. Zinc is closely related to bone metabolism, so it has a positive effect on growth and development.
Zinc and brain function:
Zinc is a key nutrient for the development of the central nervous system:
1 . The zinc-dependent enzymes are involved in brain development
2 . The zinc finger proteins have a role in the structure of the brain and in neurotransmission
3 . The zinc-dependent neurotransmitter involved in memory function of the brain
4 . Zinc is involved in the process of manufacturing a precursor of the neurotransmitters
5 . Metallothionein-III is a protein that binds the zinc in neurons
A zinc deficiency has been associated with deficiencies in attention and delayed motor development and interferes with the performance of cognitive functions.
SOURCE: The role of zinc in the growth and development of children Maria j. Salgueiro et al, Nutrition 18: 510 –519, 2002
Effect of zinc on the growth and development of infants of low birth weight
The study was conducted in 2007 on 163 low birth weight infants who were divided randomly into two groups: a group of 87 infants receiving a supplement of 10 mg/day of zinc sulfate for 6 months, a group of non-supplemented 76 infants who receive 10 mg/day of a solution of placebo.
The results obtained have shown that supplementing with zinc resulted in an increase in weight and stature and improvements in motor development. It has not been an improvement in terms of mental development.
Below are the graphs:
FIGURE 1. At the end of the study, ie after 6 months, infants who received zinc supplementation have achieved a greater weight
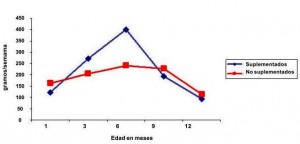
FIGURE 2. In the sixth month the group supplemented reaches higher values in terms of stature

SOURCE: Efecto del zinc sobre el crecimiento y desarrollo del niño con bajo peso al nacer RAFAEL JIMÉNEZ, M.D.1, MAYDER MARTÍNEZ Colombia Médica Vol. 38 Nº 1, 2007
RELATED STUDIES:
Effect of oral zinc supplementation on the growth of preterm infants. Islam MN, Chowdhury MA, Indian Pediatr. 2010;47(10):845-9.
The effect of zinc supplementation on linear growth, body composition, and growth factors in preterm infants. Díaz-Gómez NM Pediatrics. 2003;111:1002-9.
Effect of zinc supplementation on growth in very low birth weight infants. Ram Kumar TV, Ramji S. J Trop Pediatr. 2012;58:50-4.
Acquired zinc deficiency in a breast-fed premature infant. Guillot I, Roth B. Arch Pediatr. 2003;10:442-4.
Levels of vitamin A and E in infants of low birth weight
In this study it is determined the levels of vitamin A and E in infants of low birth weight at the time of birth (TB), at the time of ‘breast-feeding (TFF) and at the end of the post-menstrual period (TT). Were subjected to the study 35 infants average weight 1157 g (from 982 g to 1406 g) and gestational age of 30 weeks (28 to 32 weeks).
The vitamin A deficiency appears in 67.7% of infants to TB in 51.6% and 82.1% to the TFF TT.
Deficiency of vitamin E appears in 77.4% of infants to TB in 16.1% and 35.7% to the TFF TT.
SOURCE: Vitamin A and E status in very low birth weight infants. Kositamongkol S. J Perinatol. 2011;31(7):471-6.
RELATED STUDIES:
Vitamin D nutritional status in preterm infants and response to supplementation. McCarthy RA, McKenna MJ.Br J Nutr. 2012 Nov 27:1-8.
Vitamins for preterm infants. Alison Leaf, Current Paediatrics (2004) 14, 298–305
- CATEGORY For Neonate
- TAGS

 Italiano
Italiano  English
English 